At its core, fintech software development is all about creating the digital tools that power modern finance. It's the craft of building everything from the mobile banking app you use every day to the complex algorithms that drive investment platforms. Think of it as the code and engineering behind the digital evolution of money. What […]

At its core, fintech software development is all about creating the digital tools that power modern finance. It's the craft of building everything from the mobile banking app you use every day to the complex algorithms that drive investment platforms. Think of it as the code and engineering behind the digital evolution of money.

Imagine fintech software as the central nervous system for modern money. It's the invisible network of apps and platforms that connects consumers, businesses, and banks in ways we now take for granted—like tapping your phone to pay for groceries or getting a small business loan approved in minutes without ever setting foot in a bank.
This isn't just about making things more convenient. It's about a fundamental shift in how financial services work, making them more efficient, accessible, and secure for everyone. The work covers any area where technology can improve or automate a financial process.
The fintech universe is surprisingly diverse, with software designed to tackle very specific challenges. Breaking it down into these key categories really shows the sheer scope of fintech software development:
This digital reinvention has fueled a market boom. The global Fintech software market is projected to hit USD 73,021.2 million in 2025 and is on track to reach a staggering USD 134,159 million by 2033.
That explosive growth is powered by a strong 7.9% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), as innovators continue to build software that replaces clunky, outdated systems. A complete market analysis reveals the forces driving this change. In a field this critical, building software that is secure, scalable, and compliant isn't just a goal—it’s the absolute price of entry.
Behind every slick payment app or instant loan approval, there's a powerful and complex technical engine at work. The success of any fintech product truly hangs on its architecture and tech stack—these are the digital blueprints and building materials that dictate how secure, fast, and scalable it will be. Getting this combination right from the start is one of the most important calls you'll make.
Let's use an analogy: building a digital bank. An old-school monolithic architecture is like constructing the entire bank as one single, massive building. It seems simple at first, but if you need to make a small change—say, updating the software at the teller windows—you have to shut down the whole operation. It's slow, risky, and a nightmare to adapt.
That’s why modern fintech has overwhelmingly moved to a microservices architecture. In this model, the digital bank isn't one giant building; it's more like a campus of smaller, specialized offices. One handles user logins, another processes transactions, and a third manages account balances.
Each of these services runs on its own. If you need to update the transaction processing service, the other services keep humming along without any issues. This approach offers some huge advantages:
This shift in architecture is what allows fintech companies to innovate so quickly and build rock-solid systems. By breaking down huge, complex applications into small, independent parts, you can react to market demands and scale individual features without having to tear down and rebuild everything.
The engine powering this architectural revolution is cloud computing. Instead of buying, housing, and maintaining racks of physical servers, fintech companies can tap into cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure. This cloud-native approach is the perfect partner for microservices, giving companies the power to scale resources up or down in an instant.
The impact has been massive. The cloud-based fintech software market was valued at USD 25.3 billion back in 2019 and is on track to grab 45% of the market share by 2025. This explosion is all thanks to the cloud's cost-efficiency and scalability—it allows scrappy startups to compete with established financial giants without needing a massive upfront investment in hardware.
Once you've settled on an architecture, it's time to choose your tools: the technology stack. This isn't a one-size-fits-all decision. The right stack is completely dependent on what you're trying to build.
A technology stack is made up of several layers, but let’s focus on the big three: programming languages, databases, and the servers and APIs that tie it all together.
Choosing the right technology stack is critical. A payment gateway has very different needs than a data-heavy analytics platform. The table below breaks down some popular stacks to show how different tools are suited for different jobs.
| Application Type | Popular Languages | Database Choices | Key Frameworks | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Payment Gateways | Go, Java, C++ | PostgreSQL, MySQL | Gin (Go), Spring (Java) | High-throughput, secure, and low-latency transaction processing. |
| Robo-Advisors | Python, R | MongoDB, PostgreSQL | Django, Flask, TensorFlow | Complex algorithmic trading, risk analysis, and portfolio management. |
| Digital Banking Apps | Java, Kotlin (Android), Swift (iOS) | PostgreSQL, CockroachDB | Spring, Hibernate | Secure, scalable, and feature-rich platforms for daily banking needs. |
| Blockchain/Crypto | Solidity, Rust, Go | N/A (Distributed Ledger) | Truffle, Hardhat | Building decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. |
Ultimately, the goal is to pick a stack that is secure, scalable, and supported by a strong developer community. This ensures you can build a reliable product and find the talent you need to maintain and grow it over time.
Popular Programming Languages:
Database Considerations:
Fintech databases generally fall into two categories. SQL databases like PostgreSQL are highly structured and rigid, which is exactly what you want for ensuring the integrity of core financial ledgers. On the other hand, NoSQL databases like MongoDB are more flexible and scale out easily, making them great for handling huge amounts of less-structured data, like user profiles or analytics logs.
The Role of APIs and Servers:
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are the messengers that allow different microservices to talk to each other and to outside systems. They're what make it possible to connect your bank account to a budgeting app. The servers that handle all these requests are just as important. For a closer look at server options, check out our comparison of https://hiredevelopers.com/apache-http-server-vs-apache-tomcat/. And if you're curious about the decentralized tech that's reshaping finance, a great place to start is understanding what blockchain development entails.
In the world of fintech, security isn't just another feature on a checklist—it's the very foundation of your business. Think of your app as a digital bank and your security framework as its vault. A flimsy vault doesn't just put money at risk; it shatters the customer trust that keeps the whole operation afloat.
Getting this wrong is not an option. A security breach can lead to catastrophic financial losses, eye-watering regulatory fines, and a loss of customer confidence so complete it can put you out of business for good. That's why security and compliance have to be baked into your development process from day one, not bolted on as an afterthought.
The regulatory landscape can feel like a confusing mess of acronyms, but getting a handle on the key standards is non-negotiable. These rules exist for a reason: to protect consumers, stop financial crime, and keep the financial system stable.
Here are the big ones every fintech founder and developer absolutely must know:
Think of these regulations as the mandatory building codes for your digital vault. Ignoring them is like building a skyscraper on a faulty foundation—it’s not a matter of if it will collapse, but when. The stakes are simply too high to cut corners.
Beyond just ticking regulatory boxes, real security comes from a layered, "defense-in-depth" approach built right into your software's DNA. Implementing robust fintech security measures is what separates the serious players from the cautionary tales. It’s all about creating multiple barriers that an attacker would have to breach.
This means you and your developers have to start thinking like the bad guys, anticipating where the weak points might be and patching them up before they can ever be exploited.
Here are the foundational security practices that should be considered standard operating procedure for any fintech project:
| Security Practice | Description | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | This is the process of scrambling sensitive data (like passwords and financial records) into an unreadable code, both when it's just sitting on a server (at rest) and when it's moving across the internet (in transit). | It's your last line of defense. Even if a hacker breaches your servers, encrypted data is useless without the key. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Instead of just a password, MFA requires users to provide a second (or third) piece of proof that it's really them—like a code from their phone or a fingerprint. | This single measure dramatically cuts down on unauthorized account takeovers, even if a user's password gets stolen. |
| Secure Coding Practices | This means your developers are actively following established guidelines (like the OWASP Top 10) to avoid common but devastating vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS). | You're plugging security holes at the source code level, making your application fundamentally stronger against attacks. |
| Regular Security Audits | This involves bringing in outside security experts to do penetration testing and vulnerability scans. Their job is to try and break into your system, just like a real attacker would. | An unbiased, expert pair of eyes will find weaknesses and blind spots that your internal team, no matter how good, might have missed. |
Remember, integrating these practices isn't a one-and-done task. It's a continuous commitment. The world of cyber threats is always evolving, and your security measures have to evolve right along with it to keep your users—and your business—safe.
Taking a fintech product from a concept scribbled on a napkin to a full-fledged application is a journey with a very specific map. This path, what we call the fintech software development lifecycle, is a structured process that has to walk a tightrope between rapid innovation and the unyielding demands of security and compliance. It’s less about a mad dash to the finish line and more about a deliberate, step-by-step build toward a successful and trustworthy product.
This lifecycle isn't just about developers hammering away at keyboards. It’s a holistic approach that breaks down into five critical phases, each one building on the last to create a financial tool that’s both powerful and safe.
Discovery and Planning: This is ground zero. Before we even think about code, we validate the idea itself. Is there a real market need? Who are we building this for? What are the absolute must-have features, and what regulations do we need to nail from day one? It’s all about asking the hard questions early.
UI/UX Design: In the world of finance, a clunky or confusing interface isn't just an annoyance—it's a trust-killer. This phase is dedicated to creating a user experience that feels intuitive, secure, and effortless, translating complex financial operations into simple, clean steps.
Development: With the blueprints in hand, the engineers get to work. This is where the backend logic, databases, APIs, and the front-end interface come to life. Crucially, security isn't an afterthought; it’s baked into every layer of the architecture from the very beginning.
Rigorous Testing: This stage goes far beyond typical bug squashing. We're talking about intensive security audits, penetration testing to find vulnerabilities, and load testing to ensure the app doesn't buckle under pressure. Every single calculation must be flawless.
Deployment and Maintenance: The launch is just the beginning. Once the application is live, the cycle shifts. Now, the focus is on monitoring performance, listening closely to user feedback, and planning the next wave of features and improvements.
In a market as dynamic as fintech, trying to build the "perfect" application with every feature imaginable right out of the gate is a surefire way to burn through cash and time. That's why the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) strategy isn't just a good idea; it's essential.
An MVP is the most basic, functional version of your product that solves one core problem for a specific group of early users.
Think of it this way: instead of spending two years building a fully-loaded luxury sedan, you start with a skateboard. It proves the fundamental concept—getting a person from point A to B. Based on what you learn, you add handlebars (a scooter), then a small motor (a motorcycle), and eventually, you build up to that feature-rich car.
This diagram shows the three pillars that have to be rock-solid from the very first version, even in a stripped-down MVP.
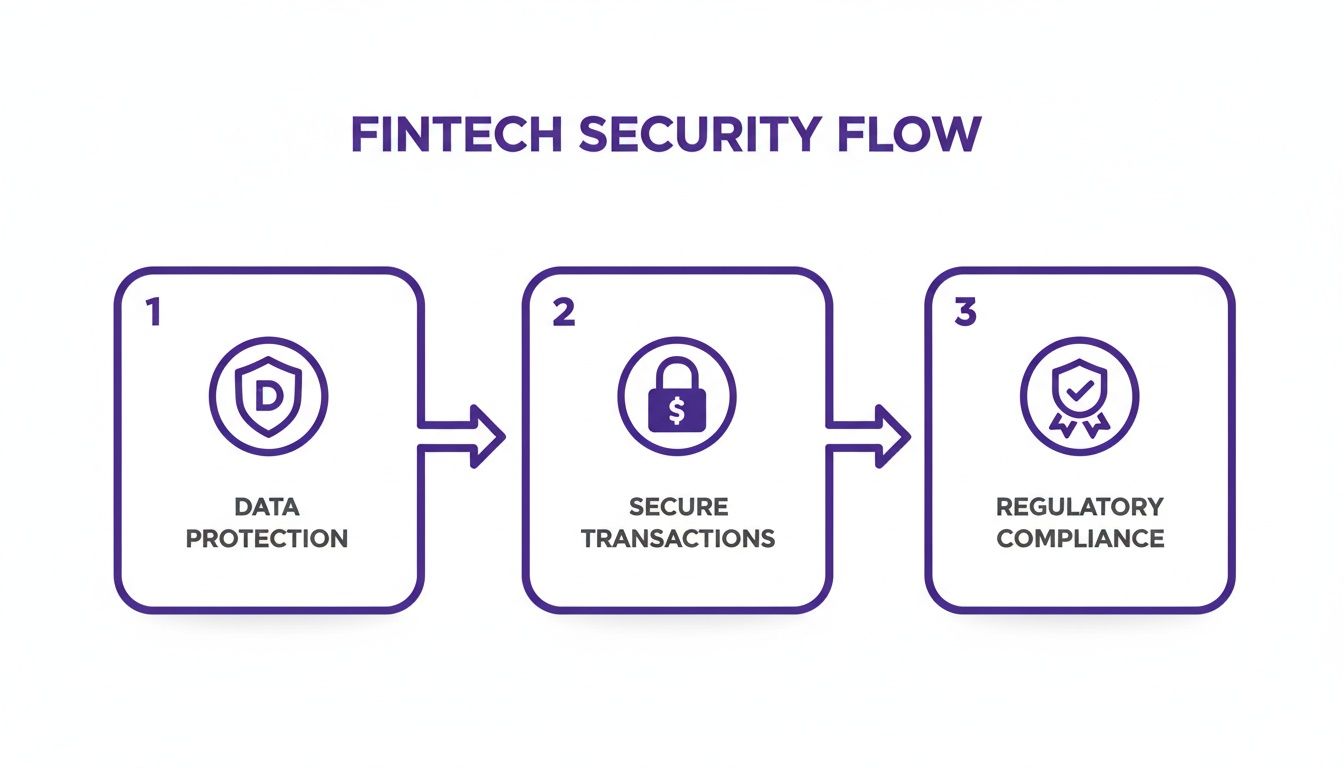
As you can see, data protection, secure transactions, and compliance are non-negotiable foundations, not features to be added later.
Let’s say you have an idea for a new budgeting app. The old way would be to spend a year or more building everything at once: bill payments, investment tracking, credit score monitoring, and savings goal features. It would be a massive, costly undertaking.
An MVP strategy completely flips that approach. Your first launch would solve just one big problem: helping users understand where their money is actually going. The only features would be linking a bank account and automatically categorizing spending. That's it.
This lean approach delivers some huge wins:
By launching a lean MVP, you can iterate and add features like bill reminders or investment tools based on real data. This agile, feedback-driven cycle is the heartbeat of modern fintech development. To dive deeper into this methodology, check out our guide on how to build an MVP.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have officially moved from the lab to the front lines of fintech software development. These aren't just buzzwords anymore; they are practical, powerful tools that are completely changing how financial services are built, delivered, and protected. Frankly, any fintech strategy that doesn't have a serious AI component is already playing catch-up.
Think of AI as a team of tireless analysts who can process mountains of financial data in a split second. This unlocks a level of efficiency and insight that’s simply not possible with human power alone.
Let's cut through the hype. AI isn't some far-off concept—it’s already running some of the most critical functions in finance today. When you look past the jargon, you can see its real impact.
Here are a few ways AI is already hard at work:
The money behind this shift is staggering. The AI fintech market was valued at USD 30 billion in 2025 and is projected to skyrocket to USD 83.1 billion by 2030. That’s a growth rate of over 20% CAGR, driven by AI's mastery of fraud detection, personalized banking, and predictive analytics. You can find more of the statistics driving fintech trends on DigitalSilk.com.
The upside of using AI is clear. It helps fintech companies work smarter, make better-informed decisions, and give customers a truly personal experience. But getting there isn't always a walk in the park.
Successfully weaving AI into a fintech product means thinking carefully about a few key things:
Despite these challenges, the competitive edge that AI provides is too big to ignore. For anyone working in fintech software development, understanding how to build, deploy, and manage AI-driven systems is no longer a "nice-to-have" skill—it's a fundamental requirement for staying in the game.
Let's be honest: the most brilliant idea and the most advanced tech stack are just hypotheticals without the right people. Assembling a high-performing team is where the rubber meets the road in fintech development. You're looking for a unique blend of razor-sharp technical skills and a deep understanding of the financial world.
A successful fintech product isn't a solo act. It's more like a symphony, where specialized roles work together to create something secure, compliant, and genuinely helpful for users.
While every project is different, there are a few roles that are absolutely essential for building a quality product from the ground up.
Getting how these roles fit together is key. For a more detailed breakdown of how these experts collaborate, check out our guide on the key roles in agile software development.
Finding top fintech talent is tough; the market is incredibly competitive. Founders usually weigh three main options: building a team in-house, hiring freelancers, or partnering with a development agency. Each has its own trade-offs in terms of cost, control, and how fast you can move.
But there's a more modern, flexible approach that's gaining a lot of traction: scaling your core team with pre-vetted, specialized talent from a dedicated platform. This hybrid model can be a game-changer.
Think about it this way: instead of spending months on a traditional hiring process, you can tap into a curated talent platform. This gives you immediate access to niche experts—like a senior blockchain developer or a machine learning engineer—for the exact duration you need them, without the long-term overhead of a full-time hire.
This strategy can slash your development timeline. Platforms like HireDevelopers.com open up a global pool of engineers who have already been rigorously vetted. You can bring a world-class developer onto your team in less than a week, giving you the specialized skills you need to innovate faster and get to market ahead of the competition.
Diving into fintech development brings up a lot of practical questions, especially for founders and product leaders looking to build something new. Let's tackle some of the most common ones we hear.
The honest answer? It varies wildly. You could be looking at anywhere from $50,000 for a straightforward MVP to over $500,000 for a complex, feature-packed platform. A few key things really drive that number up or down.
Feature complexity is the big one. A simple digital ledger is worlds apart from building a real-time payment gateway with bank-level security. The cost difference is massive.
Then there's the regulatory maze. If you're handling card payments, for example, getting PCI DSS compliant adds a significant layer of work—and cost. And of course, the size, experience, and location of your development team will heavily impact the final bill.
If I had to boil it down, I'd say the three biggest challenges are security, compliance, and scalability. Get one of these wrong, and your product is dead in the water.
First, security is everything. You're handling people's money and sensitive data, so your security has to be bulletproof. A single breach doesn't just lose data; it destroys trust, and you can't recover from that.
Next, you have to navigate a dense and constantly shifting web of financial regulations. It's a full-time job just keeping up. Finally, your system has to be built for growth from the very beginning. An architecture that works for a hundred users will crumble under the weight of a million, so you need to plan for scale from day one.
The real trick is getting all three of these right at the same time. You’re trying to build something that's innovative and easy to use, but it also has to be fundamentally secure, compliant, and ready to handle massive growth. It's a tough balancing act.
You should plan for a timeline of about 4 to 9 months to get a solid fintech MVP out the door. The biggest factor here is scope—what essential features absolutely must be in the first version?
The journey typically breaks down like this:
The whole point of an MVP is to get a secure, working product into the hands of real users as quickly as possible. Keeping that initial feature set lean is the secret to hitting your timeline and kicking off that all-important feedback loop.
Finding the right Drupal developer can make or break your project. It's that simple. We're not just talking about a content management system here; Drupal is the backbone for some of the most complex, enterprise-level digital experiences out there. For that reason, hiring a true specialist isn't just a good idea—it's essential for building a […]

When you hear "part-time developer," what comes to mind? It’s more than just someone working fewer hours. Think of them as a highly skilled specialist you bring in for a specific, high-stakes mission. Typically, they work anywhere from 10 to 25 hours per week, but their real value isn't measured in hours—it's measured in impact. […]

Hiring an engineering manager is one of the most critical decisions for a growing tech company. A great manager not only accelerates delivery but also builds a resilient, innovative, and motivated team. A poor hire, on the other hand, can introduce process bottlenecks, erode culture, and lead to high turnover among your best engineers. So, […]
