It's easy to get tangled up in the "Express.js vs. Node.js" debate, but here’s the thing: it’s not really a debate at all. They aren't competitors. In fact, they work together. Think of Node.js as the engine—it’s the powerful runtime that lets JavaScript do its magic outside of a web browser. But an engine on […]

It's easy to get tangled up in the "Express.js vs. Node.js" debate, but here’s the thing: it’s not really a debate at all. They aren't competitors. In fact, they work together.
Think of Node.js as the engine—it’s the powerful runtime that lets JavaScript do its magic outside of a web browser. But an engine on its own doesn't get you very far. That's where Express.js comes in; it's like the car's frame, steering, and pedals, giving you a practical way to actually use that engine to build something useful, like a web application.
Newcomers to backend development often get this wrong, seeing them as two technologies to choose between. The reality is that Express.js is a web application framework built on top of Node.js. It doesn't replace Node.js; it makes its powerful, low-level features much easier to work with.
You could build a server using only the raw tools Node.js provides, like its http module. But you'd quickly find yourself writing tons of repetitive code just to handle basic tasks like routing incoming requests, parsing data from forms, or managing cookies. It's a lot of work just to get to the starting line.
This is where Express.js shines.
Express handles all that low-level complexity for you. It provides a clean, structured way to manage web traffic, turning what would be a mountain of manual code in raw Node.js into just a few simple, elegant lines.
This relationship lets developers skip reinventing the wheel and get straight to building the core logic of their applications. If you want to zoom out and see how Node.js fits into the bigger picture, our guide on Node.js vs JavaScript is a great place to start.
Let’s look at a quick breakdown of how these two technologies differ in practice. This table offers a high-level summary to clarify their distinct roles.
| Aspect | Node.js | Express.js |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | A JavaScript runtime environment for executing code on the server. | An unopinionated web application framework that runs on Node.js. |
| Level of Abstraction | Low-level. Provides core modules like http and fs for servers. |
High-level. Simplifies routing, middleware, and request handling. |
| Use Case | The foundation for any server-side JavaScript application. | Building web applications and APIs efficiently and quickly. |
| Core Features | Event-driven, non-blocking I/O, package management (npm). | Routing system, middleware pipeline, template engine integration. |
As you can see, one provides the foundation, and the other builds upon it to deliver specific web-focused functionality.
The usage statistics from 2025 also paint a clear picture of this hierarchy. Node.js is used by 48.7% of developers, making it the most popular web technology overall. In contrast, Express.js is used by 19.9%. This isn't because Express is less important, but because it’s a specialized tool within the broader Node.js ecosystem.
This has real implications for hiring. A developer skilled in Express must know Node.js, but a Node.js developer might not have specific experience with the Express framework. That’s a crucial distinction for any technical leader building out a team.
To really understand the Express js vs Node js conversation, we need to break down what each one actually does. Think of Node.js as the engine room of your server. It’s the foundational environment that handles the raw, complex mechanics of running JavaScript outside of a browser.
At this low level, Node.js is busy with core server tasks:
fs module that gives you direct access to read, write, and manage files on the server. This is a must-have for any application that needs to handle data.Basically, Node.js hands you a powerful set of unrefined building blocks. You get maximum control, but you also have to assemble everything yourself, which can be a slow and complex way to build a modern web application. This is exactly where Express.js comes into the picture.
Express.js doesn't replace Node.js; it sits right on top of it. It takes all of those powerful but complicated core features and wraps them in a much simpler, more organized package. It clears away the boilerplate code, letting you and your team focus on building your application’s logic instead of reinventing the wheel with low-level server configuration.
Express introduces a set of features specifically designed for building web apps and APIs:
This layer of abstraction is a massive productivity booster. It’s no surprise Express became the go-to framework for Node.js, powering millions of applications. Performance benchmarks show it’s capable of handling over 11,202 requests per second, and its popularity is undeniable, with over 57,000 stars on GitHub. This widespread adoption makes it a safe, reliable bet for projects ranging from simple websites to intricate APIs. If you're building APIs, our guide on GraphQL vs REST API architectures offers more great context.
The Key Takeaway: Node.js gives you the engine to run a server. Express.js gives you the chassis and steering wheel to build a functional web application on that server, quickly and efficiently.
Consider a simple "Hello World" example. In raw Node.js, you have to manually parse the URL, check the HTTP method, write the response headers, and then end the response. With Express, this entire process is boiled down to a single, intuitive line of code. That small difference perfectly captures the value Express brings to the table.
When technical leaders weigh Node.js vs. Express.js, the conversation inevitably turns to speed and scalability. These aren't just buzzwords; they directly impact user experience, server costs, and whether your product can handle growth. But here’s the thing: you can't really pit one against the other in a traditional speed test. Express is built on top of Node, so it shares the same high-performance DNA.
The real difference isn't in raw execution speed, but in development speed. If you build a web app with plain Node.js, you're starting from scratch. That means manually writing code to handle every single route, parse every request, and format every response. It's a ton of foundational work that slows you down, especially when you're trying to launch an MVP or quickly add new features.
This is where Express completely changes the game. It provides a ready-made structure for all that boilerplate. With its routing system and middleware, your developers can jump straight into building the features that matter to your business. It's an abstraction layer that lets a team build, test, and ship in a fraction of the time, which is a massive competitive advantage.
One of the first questions I get is, "Doesn't Express add performance overhead?" It's a fair question, but for almost every real-world application, the answer is no. The impact is so minimal it's practically immeasurable.
Your application's true performance engine is Node.js itself, with its incredibly efficient, non-blocking, event-driven architecture. That’s what allows it to handle thousands of simultaneous connections without breaking a sweat. Express just adds a thin, lightweight layer for routing.
In my experience, performance bottlenecks in a Node.js app are almost never the framework. They’re slow database queries, long waits for external API calls, or inefficient, blocking code that your team wrote.
So, choosing Express isn't a performance sacrifice. It's a strategic trade-off: you accept a tiny, often theoretical, bit of overhead for huge gains in developer productivity and code that's far easier to manage.
When it's time to grow, both raw Node.js and Express applications scale beautifully. Again, because Express is built on Node, it inherits all of Node's native strengths for building scalable network applications.
In the Node ecosystem, scaling almost always means horizontal scaling—running multiple copies of your app and putting a load balancer in front of them. This approach works exactly the same whether you’re using Express or not.
Here are the standard strategies you'll use:
Ultimately, your ability to scale has very little to do with choosing Express over plain Node.js. The architectural principles are identical. The only real difference is how fast you can build the application you plan on scaling in the first place.
Choosing between raw Node.js and Express.js really boils down to a classic trade-off: do you need absolute, granular control, or do you need to get things done quickly? Think of it as the difference between building a car from individual parts versus starting with a high-performance chassis. For most technical leaders, the decision directly shapes project timelines, developer productivity, and how fast you can actually ship.
Let's be clear: for almost any project that involves the web, Express.js is the default, go-to choice. If you're building a RESTful API, a traditional web application, or a fleet of microservices, Express gives you the essential scaffolding you need right out of the box. Its routing and middleware are the bedrock of the Node.js ecosystem for a reason—they solve the most common backend problems so your team can focus on what makes your product unique, not on reinventing the wheel.
This isn't just a theoretical advantage; it's proven at scale. Big players like Twitter Lite built their service on Node.js with a framework similar to Express, proving it can handle the demands of a massive, global user base.
This decision tree gives a great visual overview of the thought process.
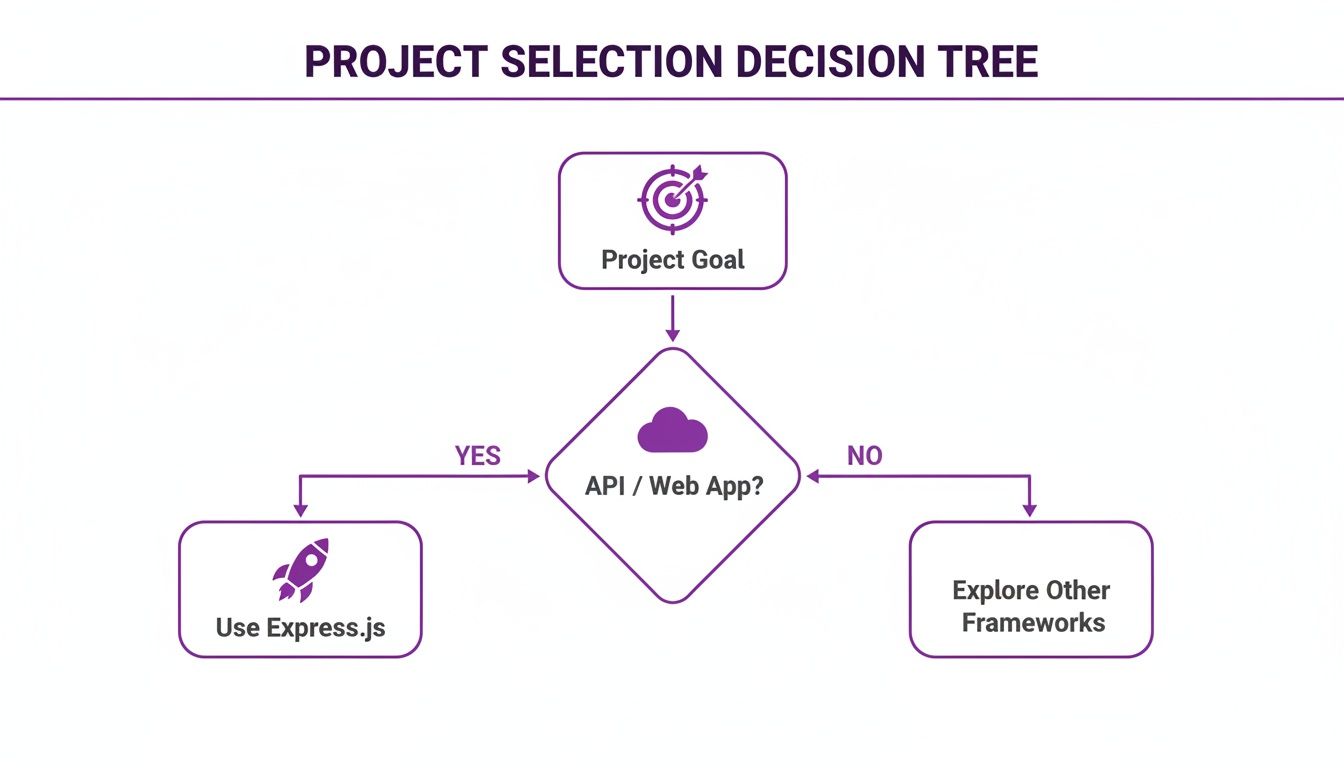
As you can see, if an API or web application is on your roadmap, the path almost always leads to Express.js.
So, are there times when you'd deliberately skip a framework? Absolutely, but they are very specific and usually don't involve building a typical web application.
Here are a few scenarios where sticking with raw Node.js makes perfect sense:
net or http modules. This gives you maximum control over sockets and data streams.Outside of these niche cases, choosing raw Node.js for a new web project is like choosing to walk when a car is available. You’ll eventually get there, but it will be a much longer and more difficult journey.
Raw Node.js offers maximum control, but Express.js delivers maximum velocity. For virtually all web applications, velocity is the winning business strategy.
This is the heart of the matter. The Express js vs Node js debate isn't about which one is "better" in a vacuum. It's about picking the right tool for the job you have today. For any business that needs to build, test, and scale a product efficiently, the battle-tested, feature-rich environment of Express.js is the pragmatic and winning choice. It makes your developers more productive, and that translates directly to a faster time-to-market.
Bringing a technical vision to life really boils down to one thing: securing top-tier backend talent. When we talk about Express.js vs Node.js, hiring managers need to look past the syntax. The best developers don't just know the tools; they know how to use them to build systems that are robust, scalable, and secure.
A truly senior Node.js and Express.js developer brings a lot more to the table than just coding chops. Their value comes from a mix of deep foundational knowledge and practical, high-level experience.
When you're vetting candidates, look for a holistic skill set. The best engineers don’t just live in one narrow specialty; they can own a feature from the initial idea all the way to deployment.
Here are the skills you should be looking for:
The difference between a mid-level and a senior developer often isn’t what they know, but how they handle ambiguity. A senior engineer can architect a solid solution even with incomplete requirements, anticipating future needs and building for resilience.
This kind of foresight is incredibly valuable and a clear sign of real-world experience.
It’s crucial to understand the difference between junior, mid-level, and senior talent to build a well-balanced team. A junior developer can knock out well-defined tasks, but a senior engineer is the one providing architectural guidance and mentorship for the whole team.
For startups and scaling teams, hiring the right senior talent can be a total game-changer. That's why a platform like HireDevelopers.com is so effective. Our rigorous, multi-stage vetting process—which combines AI screening, live assessments, and deep technical interviews—ensures you only connect with the top 1% of pre-vetted engineers. We help you skip the noise and get an expert on your team in as little as a week. To learn more, check out our guide on how to hire software engineers.
It's time to move beyond generic whiteboard problems. Your goal is to see how a candidate solves problems and what their real-world experience looks like, not whether they memorized an algorithm. While checking their performance on common Top 10 Coding Interview Questions is a decent baseline, you need to tailor your process to what you actually need.
Here are a few targeted questions to get a real conversation going:
Questions like these open up a dialogue and reveal how a candidate thinks about architecture, security, and scalability—the very qualities that define an elite developer.
When you're digging into backend development, a few questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle the most common ones about Node.js and Express to clear up any confusion and solidify the key ideas we've covered.
You absolutely can. In fact, it’s a great way to learn. Node.js has a built-in http module that gives you all the tools you need to build a web server from the ground up. Doing this gives you a real feel for how request and response cycles work under the hood.
But for any real-world application, you'll quickly find yourself writing a ton of repetitive code just to handle basic things like routing, parsing request bodies, or managing headers. That’s where a framework like Express comes in. It handles all that boilerplate, so you can stop reinventing the wheel and start building your application's features.
Not at all. While Express is the undisputed veteran and often the default choice, the Node.js world is full of fantastic frameworks. The right one for your project really depends on what you're building and what your team is comfortable with.
Here are a few popular alternatives:
Start with Node.js. There’s no substitute for understanding the core engine first. Getting a firm grip on concepts like the event loop, I/O operations, and asynchronous programming will pay dividends for your entire career.
Try building a simple server with just the http module. Once you’ve done that, moving to Express will feel like a superpower. You'll instantly see the value it provides because you've experienced the pain points it was designed to solve. Jumping straight to Express without that foundational knowledge can leave you stranded when you need to debug a tricky performance issue.
The best way to learn is Node.js first, then Express. Think of it like learning how an engine works before you get behind the wheel of a high-performance car. It just makes you a better, more capable developer.
Stable Coin hired a senior full-stack engineer with a background in mobile development.

Marketers in Demand hired two senior WordPress developers with HireDevelopers.com

Rito Labs hired two full-stack software developers with HireDevelopers.com
