A full stack developer is a jack-of-all-trades in the software world. They're the kind of engineer who can handle both what you see on the screen—the frontend—and all the complex machinery working behind the scenes—the backend. Think of them like a master builder. They don't just design the beautiful, user-friendly interior of a house; they […]

A full stack developer is a jack-of-all-trades in the software world. They're the kind of engineer who can handle both what you see on the screen—the frontend—and all the complex machinery working behind the scenes—the backend.
Think of them like a master builder. They don't just design the beautiful, user-friendly interior of a house; they also engineer the critical plumbing, electrical, and structural systems that make it all work. They have the complete skillset needed to take a digital product from a simple idea all the way to a fully functioning application.
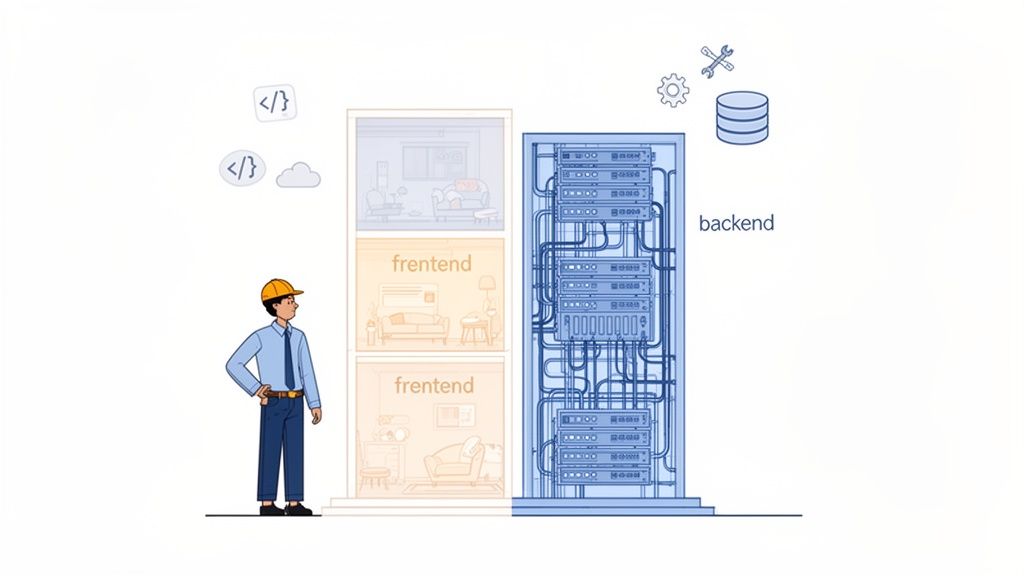
To really get what a full stack developer does, you first have to understand the "stack." A technology stack is simply the combination of programming languages, tools, and software used to build and run an application. Every app has two main components that a full stack developer needs to master.
First, there's the frontend, which is everything the user sees and interacts with. It’s the visual layout, the buttons you click, and the forms you fill out. This is often called the "client-side" because it runs right in your web browser.
Then there’s the backend, the powerful engine hidden from view. This includes the server that hosts the application, the database that stores all the information (like user accounts or product details), and the core logic that makes everything happen. This is the "server-side."
What makes a full stack developer so special is their ability to work on both sides of this divide without missing a beat. They can code an interactive user interface and then turn around and build the server-side API that sends data to that very interface. This big-picture view is what makes them incredibly valuable.
Their versatility means they can see how all the pieces connect. Instead of having a narrow focus, they can hunt down a bug whether it’s a tiny visual glitch on the screen or a complex database query failing on the server.
"Being a full stack developer isn't just a job title; it's a problem-solving mindset. It's about understanding how all the pieces of a digital product connect to create a cohesive user experience from start to finish."
This holistic approach is why demand for these pros is through the roof. The job market has seen a staggering 35% year-over-year growth in demand, with a 42% jump in job postings last year alone. Projections show over 853,000 full stack developer jobs by the end of this year, and that number is only expected to grow. You can learn more about the rising demand for full stack talent at elysiumacademy.org.
To give you a clearer picture, a full stack developer wears a lot of different hats during a project. The table below breaks down their main responsibilities, showing just how broad their skill set is.
| Area of Responsibility | Key Activities and Focus |
|---|---|
| Frontend Development | Designing and building responsive user interfaces, adding interactive features, and making sure the user experience is smooth on any device. |
| Backend Development | Writing server-side logic, managing databases, building robust APIs, and handling the application's performance and security. |
| Database Management | Creating and maintaining database structures (schemas), writing efficient queries to retrieve data, and ensuring data is always accurate and secure. |
| System Architecture | Planning the application's overall structure, selecting the best technologies for the job, and ensuring the system can grow (scale) without breaking. |
| Deployment and DevOps | Handling the process of getting the application live, setting up servers, and managing version control and automated deployment pipelines. |
Ultimately, a full stack developer is the glue that holds a project together, capable of contributing at every stage of the development lifecycle.
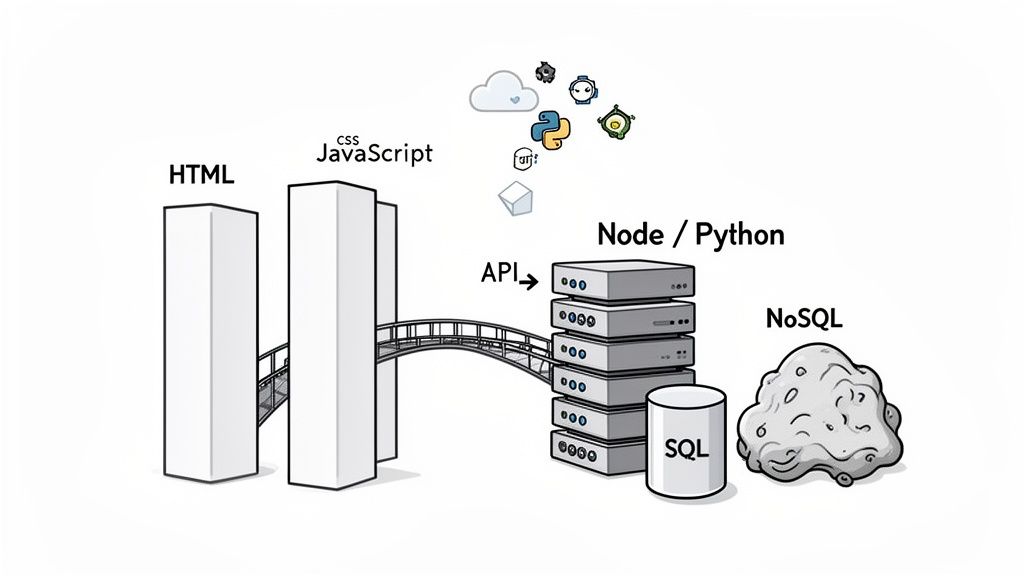
The real value of a full-stack developer lies in their ability to speak the language of an entire application's architecture. Their toolkit isn’t just a random assortment of software; it's a carefully curated set of technologies that work in concert to bring an idea to life.
Let's break down the essential pieces of this toolkit, starting from what the user actually sees and touches.
Think of the frontend as the digital storefront. It’s the part of the application users actually interact with—the buttons they click, the forms they fill out, and the content they see. To build this experience, a full-stack developer needs to be fluent in the three pillars of the web.
Of course, modern applications are far more complex than a simple static page. That’s where frontend frameworks come into play. A key part of any modern developer's skillset is proficiency with tools like the React framework or Angular. These frameworks provide pre-built components and a structured way to build sophisticated, dynamic user interfaces without reinventing the wheel every time.
Behind every sleek frontend is a powerful backend doing all the heavy lifting. This is the server-side, the engine room where the application's core logic, data processing, and security are handled. A true full-stack developer is just as comfortable here as they are on the client-side.
The key technologies here are server-side programming languages. These languages field requests from the frontend, process information, and talk to the database. Popular choices include Node.js, which brilliantly allows developers to use JavaScript on the server, and Python, prized for its clean syntax and extensive libraries.
These languages are what make the application actually do something.
Data is the lifeblood of just about every application, from user profiles to product inventories. A full-stack developer has to know how to design, manage, and query databases effectively. They typically work with two main flavors of databases:
Knowing which type of database to use for a specific job is a hallmark of an experienced developer.
A true full-stack developer embodies the Swiss Army knife of software engineering, proficient in the entire tech stack from client-side to server-side, deployment, and even DevOps basics. This versatility allows them to build complete applications solo or lead teams efficiently. Their skills are in high demand as the web development market is projected to explode to $87.75 billion in the next two years and reach $134.17 billion by the end of the decade, fueled by technologies like React (used in 32.5% of implementations). Discover more insights about this growing demand for full-stack skills.
The final pieces of the puzzle involve making all these different parts talk to each other and, most importantly, getting the application into the hands of users. This is where APIs and DevOps practices become crucial.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) act as the messengers, allowing the frontend and backend to communicate securely and efficiently. A full-stack developer often designs and builds these APIs themselves, defining the rules for how data is requested and exchanged. You can see how this works by exploring a detailed comparison of GraphQL vs REST API architectures.
Furthermore, they rely on DevOps tools to smooth out the development and deployment pipeline.
By mastering this complete toolkit, a full-stack developer can genuinely oversee a project from its earliest concept to its final launch and ongoing maintenance.
To put it all together, here’s a look at the key technologies a full-stack developer needs to know.
| Technology Category | Examples and Purpose |
|---|---|
| Frontend Essentials | HTML, CSS, JavaScript: The core languages for building any web interface. |
| Frontend Frameworks | React, Angular, Vue.js: For building complex, interactive single-page applications efficiently. |
| Backend Languages | Node.js, Python, Java, Ruby: For writing the server-side logic that powers the application. |
| Databases | SQL (PostgreSQL, MySQL), NoSQL (MongoDB): For storing, retrieving, and managing application data. |
| API Development | REST, GraphQL: For defining how the frontend and backend communicate with each other. |
| Version Control | Git, GitHub: For tracking code changes and collaborating with a team. |
| Cloud & DevOps | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Docker, Jenkins: For deploying, hosting, and scaling applications. |
Having a solid grasp of these tools across the board is what separates a good developer from a truly great full-stack engineer.
To really get what a full-stack developer does, let’s set aside the technical jargon for a moment and imagine a typical day. It’s less about being chained to a keyboard and more about a constant dance between big-picture strategy, focused coding, and collaborative problem-solving. They’re always shifting gears between what the user sees and what’s happening behind the curtain.
Their day usually kicks off not with code, but with people. Most full-stack developers are part of an Agile team, so mornings often start with a daily stand-up or a sprint planning session. They're not just there to get assignments; they're there to translate.
They take broad business ideas—say, "we need to add a new subscription feature"—and help slice them into tangible, technical pieces. This is where their holistic view is critical. They need to think through every layer: what has to change in the database, which new API endpoints need to be built, and how the user will actually interact with it on the screen.
Once the morning meetings wrap up, it's time to get hands-on. A full-stack developer might spend their afternoon building out a new feature, like a user profile page. This work often starts on the frontend, using HTML, CSS, and a framework like React to mock up a clean, intuitive layout where someone can see and update their info.
With the visual parts in place, they swap hats and jump into the backend. They might fire up Node.js to write the server logic that fetches that user’s data from a PostgreSQL database. Next up, they’ll build the API endpoint that lets the frontend and backend talk to each other, passing that information back and forth securely. This effortless pivot from client to server is their superpower.
A full-stack developer is the ultimate problem-solver on a development team. Their ability to diagnose an issue anywhere in the stack—from a misaligned button in the CSS to a slow database query on the server—makes them a central and invaluable hub for keeping a project moving forward.
Of course, no developer’s day is complete without a little detective work. A bug report lands: "Users are saying their profile changes won't save." This is where a full-stack developer’s broad knowledge really pays off. They don't just check one part of the code; they trace the data's entire journey from click to database.
Their debugging process might look something like this:
This end-to-end troubleshooting ability is what makes them so effective. While a specialist might have to flag down someone from another team, a full-stack developer can often find and fix the root cause all on their own. They see the direct line connecting their daily tasks to the final product, ensuring the application doesn’t just work, but actually delivers on its promise.
One of the biggest questions I see leaders ask is, "Should I hire a full-stack developer or bring in specialists?" It’s a critical decision that really sets the tone for a project. There's no one-size-fits-all answer here; the right choice boils down to your company's stage, the project's complexity, and where you're headed long-term.
Think of it as a classic trade-off: speed and versatility versus depth and precision. A full-stack developer gives you incredible agility, which is a lifesaver in fast-moving environments. On the flip side, specialists bring the kind of deep, focused expertise you absolutely need to build and scale complex, robust systems.
A full-stack developer is the secret weapon for teams that need to stay lean and move fast. Their ability to jump between the frontend, backend, and even the database makes them incredibly valuable, especially when flexibility is the name of the game.
You should seriously consider hiring a full-stack developer if you're:
A full-stack developer's true power on a small team is their ability to crush communication bottlenecks. They can make smart architectural decisions on the fly because they don't need to check in with separate frontend and backend engineers—they understand how all the pieces fit together.
This decision tree helps visualize that core choice between hiring for flexibility or for specialized depth.
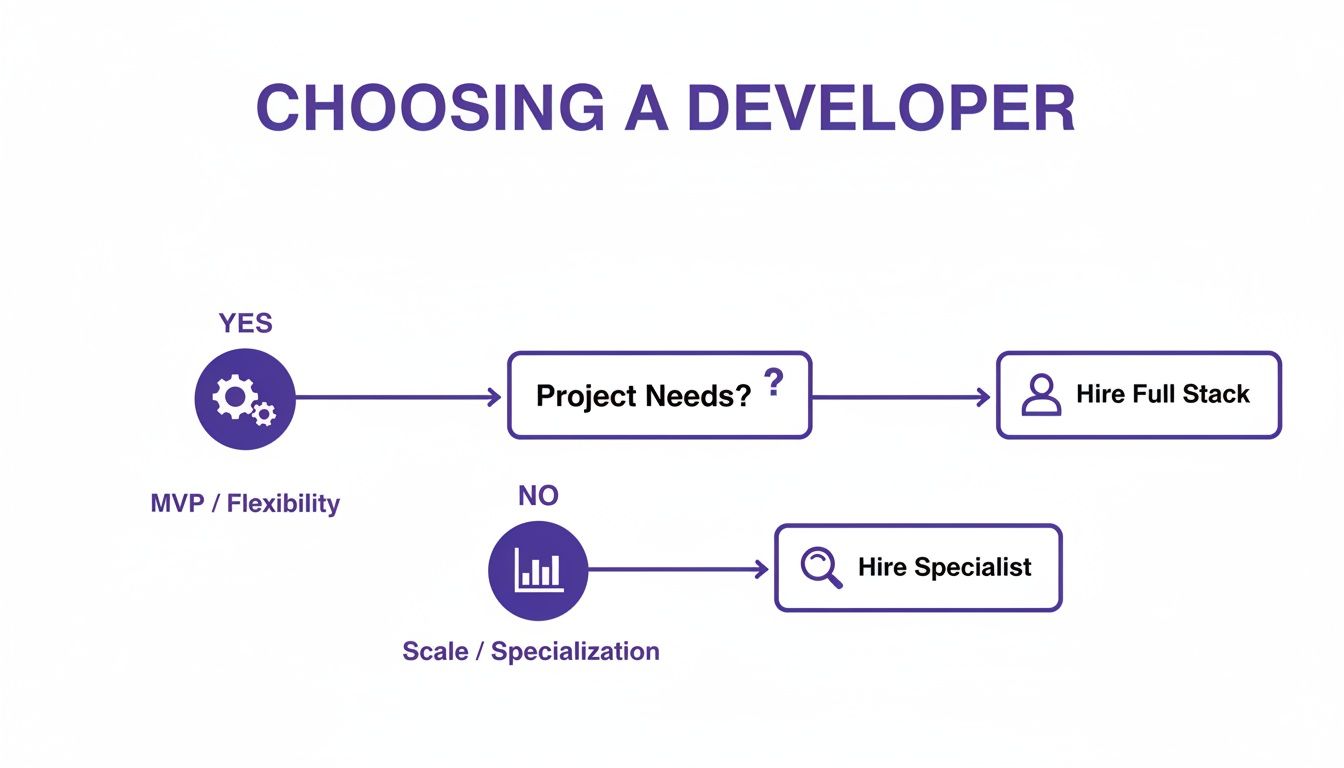
As the flowchart shows, if your main goal is to build an MVP or keep your team agile, a full-stack developer is almost always the right call.
As your project matures and the stakes get higher, the need for deep, specialized knowledge becomes impossible to ignore. This is the point where hiring dedicated frontend and backend developers isn't just a good idea—it's a strategic necessity.
You should pivot to hiring specialists when you find yourself:
Ultimately, the decision aligns with your project's lifecycle. Full-stack developers are phenomenal for getting you off the ground and finding your footing. Specialists are the ones who help you grow, scale, and dominate your market. You can learn more about how these different roles in agile software development work together to create a successful product.

Let's be honest: finding a true full-stack developer is tough. The title gets thrown around a lot, but the skillset is rare. To spot the real deal—someone genuinely skilled across the entire application—you need a hiring process that digs much deeper than matching keywords on a resume.
It all starts with their portfolio. A top-tier candidate's work should tell a complete story. Don't get distracted by a polished UI; look for proof of solid backend engineering. The best portfolios show clear ownership of both frontend elegance and backend muscle.
A project with a custom-built API, a well-thought-out database schema, and a great user experience is a huge green flag. It shows they can think like an architect, not just a programmer.
When you're looking at a candidate's past projects, push past the surface-level looks and zero in on functionality and architecture. Your mission is to confirm they can genuinely connect what a user does on the screen with what happens on the server.
Keep an eye out for these tell-tale signs:
This kind of portfolio review helps you separate the developers who can truly integrate technologies from those who've just dabbled.
Once you get to the interview, you have to test for problem-solving and system design, not just technical trivia. Anyone can memorize syntax; architecting a system that can grow is the real challenge. Ditch the "what" questions and focus on "how" and "why."
The best interview questions force a candidate to think like a CTO. They aren't about finding a single correct answer but about evaluating their thought process, their ability to handle trade-offs, and their vision for building resilient software.
Instead of asking a developer to define a term, give them a real-world problem to solve. Here are a few questions that cut to the chase:
These kinds of questions give you a window into how they'll perform when things get complicated on the job.
The reality is that this level of deep vetting takes a lot of time and requires technical expertise that many hiring managers simply don't have. It's a full-time job on its own, which is why so many companies struggle to fill these crucial roles. This is exactly the problem that platforms like HireDevelopers.com were built to solve.
By putting candidates through a rigorous, multi-stage vetting process, they do the heavy lifting for you. Candidates are typically screened with AI resume analysis, live soft-skills assessments, and in-depth technical interviews run by subject matter experts. This process is designed to ensure that only the top 1% of applicants ever reach your inbox. For a deeper dive into hiring strategies, our guide on how to hire software engineers is a great resource.
This pre-vetted approach lets you skip the noise and connect directly with proven, elite full-stack talent, so you can hire with confidence and get back to building your product.
Even after laying out the skills and responsibilities, a few questions always pop up—both from folks looking to hire and those looking to become full-stack developers. Let's clear up some of the most common ones.
Not quite, though the terms get thrown around together all the time. Think of it like this: software engineer is a big umbrella term. It covers anyone who applies engineering principles to create software.
A full-stack developer is a specific type of software engineer—one who specializes in building a web application from top to bottom. They handle everything from the part you see in your browser to the server and database that make it all work.
So, while every full-stack developer is a software engineer, not every software engineer is full-stack. You have software engineers who specialize in building mobile apps for iOS and Android, others who work on the software inside your car (embedded systems), and some who create video games. They all use different tools and tackle different problems.
The real difference is focus. A full-stack developer is a software engineer with a deep, end-to-end understanding of how to build for the web. That complete perspective is what makes them so valuable.
There's no magic answer here. The "best" stack is the one that fits the job you're trying to do. It all comes down to the project's goals, how big it might get, and what the rest of the team already knows.
That said, some stacks are incredibly popular for a reason, and learning one is a great way to get started.
If you're just starting out, my advice is to pick one stack and really get to know it. Once you understand the core ideas of how they fit together, you’ll find those skills transfer surprisingly well to other stacks.
Nope. A formal CS degree is absolutely not a deal-breaker for becoming a great full-stack developer.
A degree can give you a solid theoretical background, which is great, but what companies really care about is what you can build. Can you actually ship a working product?
Many of the best developers I know are self-taught or came out of coding bootcamps. A killer portfolio with a few real, start-to-finish projects will impress a hiring manager far more than a piece of paper. At the end of the day, your ability to solve real-world problems with code is what counts.
Nearshore outsourcing is a smart way to hire talent from nearby countries. It’s the perfect middle ground between hiring expensive local teams and managing the headaches of working with people on the other side of the world. Think of it as tapping into a world-class talent pool that’s practically in your backyard. Understanding Nearshore Outsourcing […]

Partnering with an external team to handle your software development isn't just a trend; it's a strategic move that gives you instant access to a global pool of experts. It’s how you can scale your team on demand, plug critical skill gaps, and get your product to market faster, all without the drawn-out process and […]

Choosing the right software development team structure isn’t just an HR exercise—it’s the architectural blueprint for your entire project. It fundamentally defines how your people communicate, collaborate, and ultimately, create value. Get it right, and you'll see a boost in everything from development speed to team morale. Get it wrong, and you'll be fighting friction […]
